Understanding nproc; A Powerful Tool for CPU Information in Linux
When it comes to optimizing performance and resource allocation on Linux systems, having accurate information about the available CPU resources is crucial. The nproc command is a powerful tool that provides quick and convenient access to this information. In this technical document, we will explore the nproc command, its usage, and the valuable insights it offers for system administrators and developers.
Table of Contents
What is nproc?
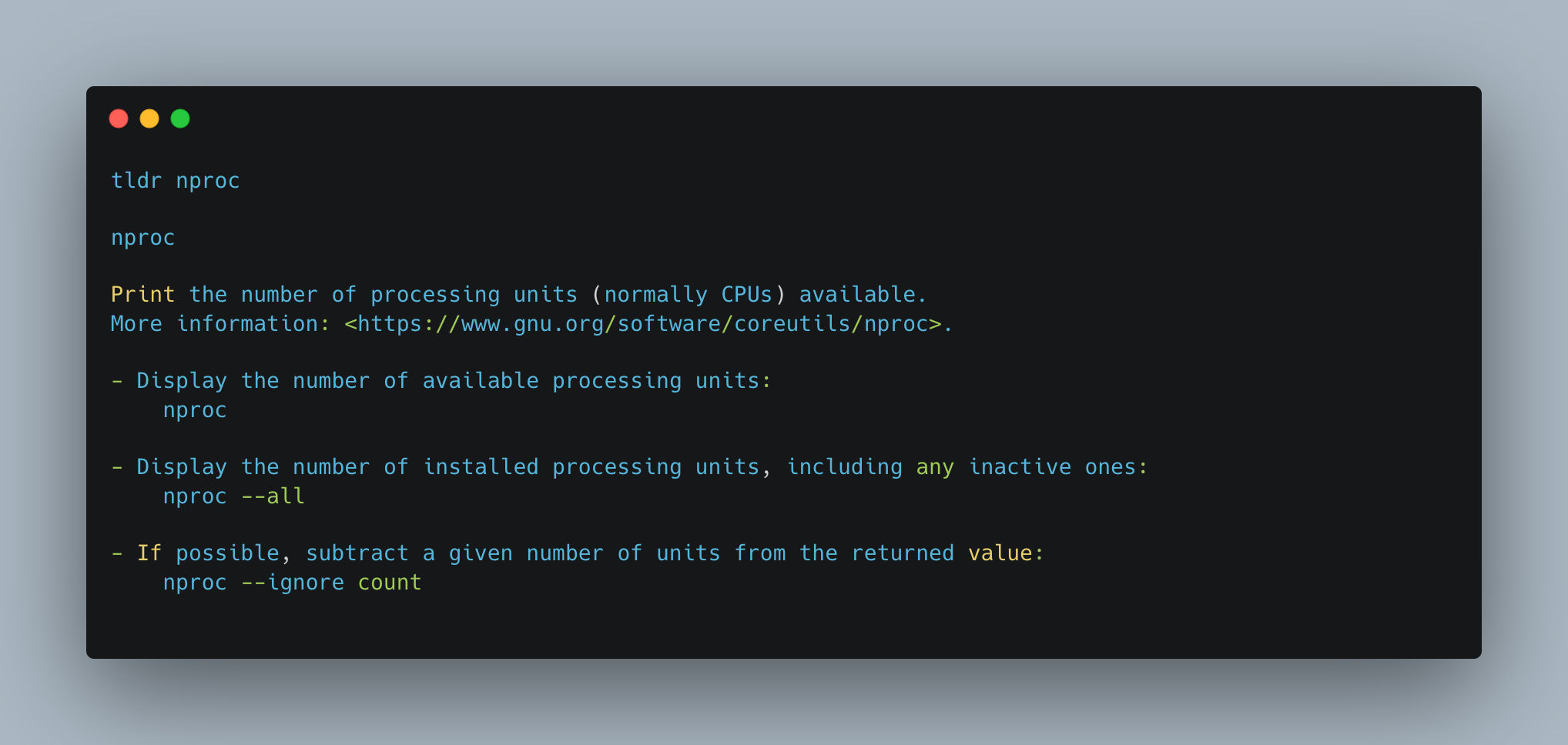
The nproc command is a utility available in most Linux distributions that displays the number of processing units available on the system. It retrieves this information by querying the /proc/cpuinfo file, which contains detailed information about the system’s processors.
Retrieving the Number of Processing Units
To obtain the number of processing units using nproc, simply execute the command without any arguments:
1
nproc
or
1
nproc --all
The output will be a single integer representing the number of processing units or CPU cores available on the system. This information is valuable for tasks that involve optimizing resource allocation, such as parallelizing software applications, load balancing, or determining the optimal number of threads to utilize.
Examples of Usage
Specifying Maximum Parallelization
One common use case for nproc is to determine the maximum level of parallelism when running computationally intensive tasks. By limiting the parallelization to the number of available CPU cores, you can ensure optimal resource utilization without overwhelming the system.
For instance, in a makefile, you can use nproc to set the maximum number of concurrent jobs for building a project:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Set the maximum number of jobs to the number of available CPU cores
JOBS := $(shell nproc)
.PHONY: build
build:
$(MAKE) -j$(JOBS) targets
This ensures that the build process utilizes the maximum available CPU resources while preventing excessive parallelization that could hinder performance.
Load Balancing
Another use case for nproc is load balancing. By knowing the number of CPU cores, you can distribute tasks or workloads evenly across available processors, optimizing resource utilization and improving overall system performance.
Load balancers and task schedulers can leverage nproc to make informed decisions on how to distribute workloads effectively. They can assign tasks to specific CPU cores or adjust thread or process affinity based on the available resources.
Hardware and Software Configuration
nproc can also assist in hardware and software configuration. For example, when compiling certain software packages, you might need to specify the number of threads to use for parallel compilation. By setting this value to the output of nproc, you ensure efficient utilization of available CPU cores:
1
./configure --jobs=$(nproc)
This ensures that the build process utilizes all available CPU cores during compilation, reducing build times and increasing productivity.
Conclusion
The nproc command is a valuable tool for retrieving CPU information and optimizing resource allocation in Linux systems. By providing the number of processing units or CPU cores available, nproc enables effective load balancing, parallelization, and hardware/software configuration.
System administrators, developers, and anyone working with Linux systems can leverage the insights provided by nproc to optimize performance, maximize resource utilization, and enhance overall system efficiency.
So next time you need to determine the number of available CPU cores or set the level of parallelism for a task, remember the power of nproc and make informed decisions based on the valuable CPU information it provides.